How to Apply Six Sigma Methodology in Your Project Management
Contents page
- Understanding Six Sigma
- When to Use Six Sigma Methodology?
- Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma
- Do I Need Six Sigma Certification?
- Six Sigma and Project Management—A Vital Intersection
- The Process—How to Apply Six Sigma
- What's the Best Software for Six Sigma?
- Overcoming Challenges in Implementing Six Sigma
- Conclusion
In today's competitive business environment, the fusion of Six Sigma methodology with project management has gained increasing attention and relevance. This combination creates a potent tool that enhances efficiency, improves quality, and delivers cost-effective results.
This article provides an in-depth look into how Six Sigma's powerful, data-driven methodology can transform your approach to work management.
Understanding Six Sigma
To better understand what role Six Sigma plays in improving business processes, it's a good idea to dive into the most important Sigma concepts.
In general, Six Sigma is a methodology that aims to improve the quality of business processes, products, and services by reducing defects and variation. In the Six Sigma method, you operate on three levels:
Using statistical tools and techniques.
Identifying and eliminating the root causes of problems.
-
As a result, Sigma's processes improve customer satisfaction, increase productivity, and reduce business costs.
That's the official definition, so let's take a look at Six Sigma in a more friendly way. Six Sigma implementation may not be easy for beginners. But once you know how to do it right, it'll be a piece of cake.
Definition of Six Sigma
Six Sigma, initially developed by Motorola in the 1980s, has become a globally recognized set of techniques and tools for process improvement. At its core, Six Sigma is a data-driven approach that aims to eliminate defects and reduce variability in any business or lean process.
The ultimate goal of Six Sigma is to deliver near-perfect products or services to the end user. In more advanced terms, this quality improvement methodology strives for a statistical measure of 3.4 defects per million opportunities, symbolized by the Greek letter sigma (σ). But that's a definition for scientific minds.
Principles of Six Sigma
Understanding the principles of Six Sigma is crucial to apply them effectively in high-level management. These principles form the bedrock of Six Sigma's methodology and provide a framework for achieving process improvements.
Here are the main tenets of Six Sigma:
-
Customer focus: Six Sigma revolves around understanding and meeting customer requirements. It stresses that quality is defined by the customer, and thus, all improvements must contribute to meeting or exceeding customer expectations.
-
Data-driven decision making: Six Sigma leverages statistical analysis to quantify process performance, identify issues, and validate the effect of changes. This principle eliminates guesswork and hunches, allowing decisions to be made based on solid data.
-
Process optimization: this principle emphasizes that quality must be built into processes. You can achieve quality improvement by identifying and removing the causes of defects, and minimizing irregularities in processes.
-
Proactive management: Six Sigma encourages proactive problem-solving and process improvement. Rather than waiting for issues to emerge and then reacting, Six Sigma promotes the anticipation of problems and the implementation of preventive measures.
-
Collaboration: Six Sigma recognizes that process improvement is a team effort. It necessitates the involvement and collaboration of everyone within the organization, from top-level management to frontline staff.
In general, In Six Sigma, customer satisfaction is the priority towards which you're aiming. And all that happens along the way is supposed to bring you closer to that satisfaction.
When to Use Six Sigma Methodology?
Six Sigma methodology is best utilized in situations where there is a need for process improvement, defect reduction, and achieving high levels of quality and efficiency. If you wonder whether Six Sigma is good for your business, you can ask yourself whether things go as planned or if you need to enforce changes.
Is there a high defect rate in your processes? Do the outputs lead to inconsistent results causing significant variation? Are there any financial problems? Are processes in your company long, tiresome, and ineffective?
In general, if you're facing some organizational obstacles, or need to revamp current practices, then Six Sigma is for you.
Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma
You may be familiar with the two types of methodology. Although they both aim at quality improvement, they have some key differences. Lean Six Sigma evolved by combining Six Sigma principles with Lean manufacturing concepts, which originated from Toyota's production system.
Lean Six Sigma method also aims to reduce defects and variation. It goes a step further by targeting process waste and inefficiencies to achieve optimal performance. Lean principles aim to eliminate activities with no value and streamline processes.
In addition to the statistical tools from Six Sigma, Lean Six Sigma employs various Lean tools like Value Stream Mapping, 5S, Kanban, and Kaizen to identify and eliminate process waste and improve flow.
So, the main difference between Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma is that the latter focuses on reducing defects and process variation, while Lean Six Sigma also targets process waste and efficiency to maximize customer value.
Is Six Sigma Better Than Lean Six Sigma?
Whether Six Sigma is better than Lean Six Sigma depends on several factors. To choose the right one for your projects, you should consider four main elements:
-
Organizational goals: you have two options—the first one is to improve product or service quality and reduce defects. Here, Six Sigma might be the more appropriate choice. On the other hand, if you want to achieve efficiency gains and minimize waste but keep quality, Lean Six Sigma will be better.
-
Industry and process type: different industries and processes have distinctive requirements. Some may benefit more from the statistical rigor and defect reduction focus of Six Sigma, while others may find Lean principles more applicable to their operational challenges.
-
Project scope: large, multifaceted projects might benefit from a Lean Six Sigma approach to streamline the entire process. Smaller, specific problem-solving efforts may find Six Sigma's statistical tools more suitable.
-
Available resources and expertise: consider the organization's existing skill sets and resources. If your employees are already familiar with Lean principles or statistical analysis, it might make sense to leverage that knowledge when selecting the methodology.
In practice, many organizations find value in combining both methodologies, employing Lean principles to identify and eliminate waste, and Six Sigma tools to achieve quality and defect reduction. This integrated approach, often referred to as Lean Six Sigma, provides a comprehensive toolkit for process improvement.
Above all, to decide which of the quality management methods is best for you, it's crucial to consider your organization's specific needs and objectives because each approach brings unique strengths to the table.
Do I Need Six Sigma Certification?
Six Sigma certification is a formal recognition of the knowledge and expertise in Six Sigma methodologies. It signifies that you've successfully completed training and demonstrated proficiency in applying Six Sigma techniques and tools. Is it necessary? It depends.
Why obtain official Six Sigma certification? Because Six Sigma expertise validates your expertise in process improvement methodologies, increasing your employability and potential for career advancement. It also benefits organizations by ensuring they have skilled professionals capable of driving significant improvements and achieving higher levels of efficiency and quality. It's a win-win deal for both sides.
There are several reputable organizations that offer professional and best Six Sigma certification courses, such as American Society for Quality (ASQ), International Association for Six Sigma Certification (IASSC), Project Management Institute (PMI). Or you can check with ASQ local chapters and universities for on-site training with Six Sigma programs.
Six Sigma and Project Management—A Vital Intersection
If it wasn't for Six Sigma strategies, today's world of team leading wouldn't be so advanced. We also wouldn't have so many great tools for planning and team collaboration. Take a look at how Six Sigma quality contributes to worldwide success for the biggest brands.
Value of Six Sigma in Project Management
The application of Six Sigma delivers significant value. By emphasizing data-driven decision-making, it provides a robust framework for identifying, analyzing, and solving problems. This approach can lead to more predictable project outcomes, increased efficiency, and reduced project costs.
For example, the Six Sigma methodology can help streamline processes and eliminate unnecessary activities, thus reducing waste and saving time. It can also enhance customer satisfaction by improving the quality of project outputs. Through the proactive management of potential issues and risks, Six Sigma can help ensure that projects are delivered on time and within budget.
Case Studies of Six Sigma in Project Management
One of the best ways to understand the impact of Six Sigma in project management is through real-world examples. One such instance is General Electric (GE), which has saved billions of dollars by implementing Six Sigma. GE incorporated Six Sigma process into its management practices to improve quality, reduce waste, and increase customer satisfaction. This comprehensive approach to quality and project management has been credited as a key driver of GE's remarkable success.
Another example is Boeing, which used Six Sigma to reduce manufacturing errors and increase efficiency in its production processes. By focusing on defect prevention, Boeing significantly improved its product quality and customer satisfaction.
These examples demonstrate that regardless of industry or company size, incorporating Six Sigma into project management practices can lead to significant business transformations.
The Process—How to Apply Six Sigma
The Six Sigma process may seem complex. However, it comprises several easy-to-follow steps that will help you in creating process maps
DMAIC in Six Sigma
The DMAIC model, standing for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control, serves as a roadmap for process improvement in Six Sigma. This structured approach helps to optimize their management process. There are five phases to follow:
1. Define: the first step involves defining the problem or project goal. This includes understanding the customer's needs, setting objectives, and identifying the process that needs improvement.
2. Measure: in this phase, you collect the baseline data to measure the current performance of the process. This gives a clear picture of the existing situation and serves as a benchmark against which you can measure improvements.
3. Analyze: you can now analyze the data you collected in the measure phase to identify the root causes of defects or issues. You can use various statistical tools and techniques to understand the relationship between different process variables.
4. Improve: based on the analysis, you develop solutions and test them to address the root causes of the identified issues. The goal here is to eliminate or reduce defects and improve process performance.
5. Control: in the final phase, you standardize the improved process, and implement control plans to ensure that the improvements are sustained over time. This involves monitoring the process and making necessary adjustments to maintain performance.
Existing Process Improvement vs. New Processes
When you apply the Six Sigma process, you can also choose the DMADV phases. DMADV is a bit different than DMAIC. It stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify.
DMAIC is used to improve existing processes that have problems or need enhancements, while DMADV is used to create new processes or products from scratch, ensuring they meet customer requirements.
Both methodologies are essential components of the Six Sigma toolkit and are chosen based on the nature of the project and the specific improvement goals.
Roles in Six Sigma
The Six Sigma methodology includes various roles with distinct responsibilities, akin to the martial arts belt system. These roles are integral to the successful application of Six Sigma in project management.
Here are all the belts you can gain through professional training and Sigma certifications:
- White Belts: this is the entry-level certification and provides a basic understanding of Six Sigma principles and concepts. White Belt holders often support Six Sigma projects or work as team members. It's also a good basis for getting a Six Sigma Yellow belt.
- Yellow Belts: Six Sigma yellow belt certification involves a more comprehensive understanding of Six Sigma model and its applications. Yellow Belts usually assist Sigma Green Belt and Black Belts in process improvement initiatives.
- Green Belts: Six Sigma Green Belt refers to employees trained in Six Sigma methods who work on projects part-time, alongside their regular job responsibilities.
- Black Belts: Black Belts are full-time project leaders who supervise and support the Green Belts. They have a deeper understanding of Six Sigma tools and techniques and often play a crucial role in implementing improvements.
- Master Black Belts: Sigma Master Black Belt belongs to experts in Six Sigma who oversee Black Belts and ensure that Six Sigma methodologies are correctly implemented. They often report directly to executive management and guide the strategic direction of Six Sigma initiatives within the organization.
Tools and Techniques
The application of Six Sigma in project management involves a suite of tools and techniques designed to drive process improvement. These include:
-
Process Mapping: this technique helps visualize the current process, identify potential areas of improvement, and monitor the impact of changes.
-
Root Cause Analysis: tools like the Fishbone diagram or the 5 Whys technique are used to identify the root cause of defects, rather than just addressing symptoms.
-
Statistical Analysis: techniques such as regression analysis, hypothesis testing, and control charts are used to analyze data, identify patterns, and validate the effectiveness of changes.
👉 PRO TIP: use planning and collaboration tools, such as TimeCamp Planner, to map your processes, organize workflow, and analyze project data to avoid roadblocks.
What's the Best Software for Six Sigma?
The best software for Six Sigma can vary depending on specific project needs, the complexity of the data analysis, and individual preferences. There are many advanced software tools commonly used in Six Sigma projects to facilitate data analysis, process improvement, and statistical calculations. These, however, may have a steep learning curve.
To simplify and automate work, you can opt for a user-friendly app with an intuitive design, such as TimeCamp Planner. It's an easy-to-use software for planning all work-related processes.
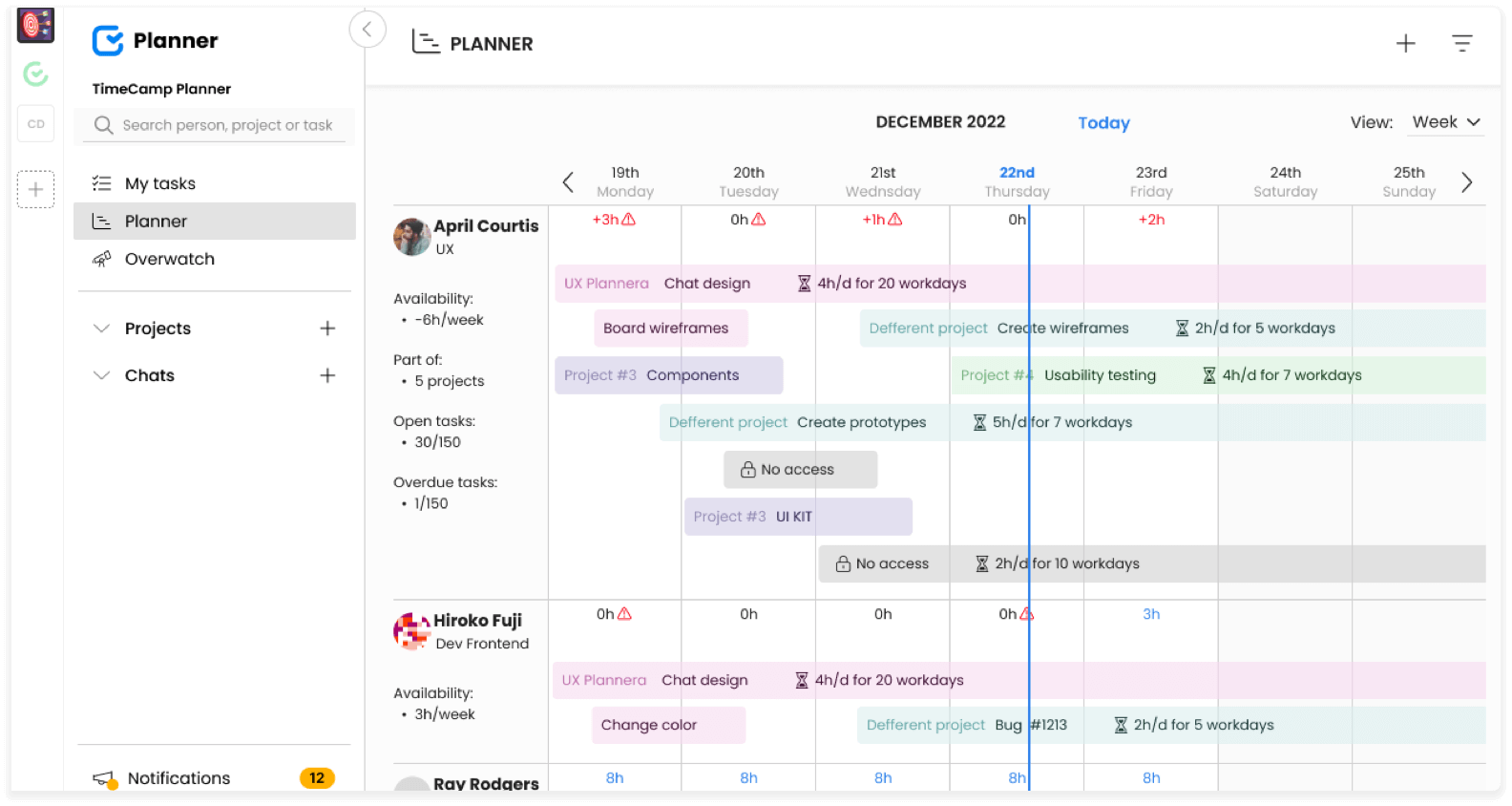
You can easily map out all the actions you need to perform during your Six Sigma project lifecycle:
-
Define or design—whether you're working on new projects or want to improve existing processes, TimeCamp Planner offers features that allow you to easily start creating the roadmap for your issue. You can choose from Kanban, Gantt chart, task list, timeline for project schedules, or Calendar view and adjust them as you need with assignees, tags, to-do lists, descriptions, attachments, comments, or make tasks recurring. That allows to create a personalized flow of work.
-
Measure—real-time dashboard shows the performance of all project teams and efficiency of the processes you've created.
Additionally, if you connect Planner to TimeCamp's automatic time tracker, you'll easily measure profitability and productivity. -
Analyze—since you have everything in one place, it's easy to check on progress, and project performance and see if you're on track. Each task card allows you to track due dates and the percentage of project completion along with team members' engagement to avoid roadblocks.
-
Improve—watching the performance from a single hub with visualization tools like Flowchart and Kanban allows you to find areas that need improvement.
-
Control— make check-ups via group or individual chat, comments and notes within a task, or video call. The overall access to all your projects lets you organize work in the most productive way.
If you use TimeCamp Planer along with Six Sigma practices, it can help you manage all workload and by monitoring it in real-time, develop key metrics for quality control in your business.
CTA: Simplify your improvement processes with TimeCamp Planner!
Overcoming Challenges in Implementing Six Sigma
Since Six Sigma can be challenging, even for the owners of Sigma Black belt, it's good to be prepared for difficult situations. You can treat them as an opportunity for growth and learn to tailor the quality management processes in your company to the demands of your client for better results.
Potential Roadblocks
While the implementation of Six Sigma can yield significant benefits, it's not without challenges. Potential roadblocks can include resistance to change, inadequate training, lack of resources, and absence of executive buy-in.
Strategies for Successful Implementation
To overcome these challenges and ensure successful Six Sigma implementation, you can employ several strategies:
-
Securing top management support: achieving buy-in from top management is crucial as their support can drive organizational commitment to Six Sigma initiatives.
-
Providing adequate training: ensuring team members are properly trained in Six Sigma methodologies is fundamental for successful implementation.
-
Aligning projects with business strategy: Six Sigma projects should align with the overall business strategy to ensure they contribute to the organization's objectives and deliver measurable results.
-
Quality assurance: use the right tools that correspond to Sigma processes in your team to ensure continuous improvement.
Conclusion
The application of Six Sigma methodology in project management can significantly enhance the efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness of projects. Its principles provide a robust framework for identifying, analyzing, and solving problems, contributing to more predictable project outcomes.
As businesses continue to strive for excellence, the integration of Six Sigma into project management strategies offers a promising avenue for continuous improvement and sustainable success.