How to Apply Critical Path Method in Project Scheduling
Contents page
- A Closer Look at Project Scheduling
- Understanding the Critical Path Method
- The Basic Elements of the Critical Path Method
- How to Implement the Critical Path Method in Project Scheduling?
- Critical Path Method Example
- Real-life Applications and Case Studies of the Critical Path Method
- The Role of Software Tools in Applying CPM
- Tips for Project's Critical Path Method
- Use Critical Path for Better Project Management
In today's dynamic business environment, the ability to efficiently plan, coordinate, and execute projects is paramount. Central to this is project scheduling—a crucial facet of project management that dictates the timeframe and order of project activities.
Among the various methodologies developed to streamline project scheduling, the critical path method (CPM) has emerged as a significant and widely used tool. Here's your short guide on the CPM and how you can use it for effective project planning.
A Closer Look at Project Scheduling
Since the critical path method is a method of scheduling, let's start from the basics—what is project scheduling?
Project scheduling is the process of creating a timeline for a project. It involves identifying all of the tasks that need to be completed, estimating start and due dates, and sequencing them in a logical order. It also involves identifying and managing task dependencies and allocating resources to tasks.
Effective project scheduling is essential for project success. It helps to ensure that the project is completed on time and within budget, and that all of the project's deliverables are met. A good schedule can also help to improve communication and collaboration within the project team, and identify and mitigate potential risks.
Understanding the Critical Path Method
What is the critical path in project management? The critical path method, or CPM, is a step beyond traditional project scheduling techniques. It was developed in the 1950s by Morgan R. Walker and James E. Kelley Jr. and is based on the PERT technique created by the US Army.
At its core, the CPM is a mathematical algorithm that calculates the longest sequence of planned activities for the project to be completed on time. This path, known as the "critical path," assists managers in determining the shortest possible duration for completing a project.
By identifying the crucial activities that directly influence the project timeline, the CPM empowers project managers to enhance project efficiency and foster better resource management. It assists in prioritizing tasks, reducing slack time, and handling potential delays, thereby maximizing productivity.
This project management technique can be used for projects of all sizes and complexity. It is especially useful for complex projects with many tasks and dependencies.
The Basic Elements of the Critical Path Method
The functionality of the critical path method is based on four key elements:
-
List of activities: Activities represent the work and tasks that need to be done in order to complete the project. Activities can be simple or complex, and of any duration. These are usually categorized with the work breakdown structure (WBS)—a way of organizing project tasks into smaller elements.
-
Duration estimates: Start and end dates of each activity.
-
Dependencies: How activities are connected with each other in the entire project.
-
Critical path: The longest sequence of activities that must be completed on time in order for the project to be completed on schedule.
Other elements of the critical path method may also include such factors as:
-
Precedence relationships. These help determine the order in which tasks should be executed, as some can only start when others are completed, while some can run in parallel.
-
Float or slack. Float is the flexibility in scheduling non-critical tasks without delaying the project. Tasks on the critical path have zero float, while non-critical tasks have positive float.
-
Early start and late start times. These are calculated for each task to determine the earliest and latest times a task can start without delaying the project.
-
Total float. It's the maximum time that a non-critical task can be delayed without affecting the project's completion.
Since the critical path analysis used in today's project management differs from the original, you can experiment with the available resources to create your ideal critical path method process.
How to Implement the Critical Path Method in Project Scheduling?
Implementing the critical path method in your project scheduling requires careful planning and precise execution. Here's a step-by-step guide to assist you in effectively applying CPM to your project management process.
1. Define the Project Scope
The first step involves defining your project's scope, which includes outlining the project goals, deliverables, tasks, costs, deadlines, and resource constraints. This will provide you with a clear picture of what you need to achieve and what you already have.
2. Break Down the Project into Tasks
Next, break down the project into smaller, manageable tasks or activities. This process, known as Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), simplifies project management by turning a large project into a collection of smaller tasks.
3. Estimate Task Duration
Once you've outlined the tasks, estimate the time each task will take. This will help you understand the project's timeline better and set an accurate project completion date.
4. Identify Task Dependencies
After estimating the task duration, identify dependent tasks. Some tasks can't start until others are completed. Some are parallel tasks and can run at the same time.
Understanding these dependencies is crucial for effective project scheduling so all the project activities are synchronized, and you can achieve the earliest possible completion date.
5. Draw the Network Diagram
Now, with all the tasks, their duration, and dependencies in hand, you can draw a network diagram. This diagram will provide a visual representation of the project's workflow, aiding in better understanding and management.
6. Identify the Critical Path
Lastly, calculate the longest path through the network diagram—this is your critical path. It represents the shortest time in which the project can be completed.
You can either use the critical path software or draw the critical path manually. However, the right tool will help you find the critical path best for the whole project and prepare for project risks.
7. Update the Project Schedule as Required
Once the project kicks off, keep updating the project schedule as needed. Changes in project scope, task duration, and resources can affect the critical path. In general, any modifications to the critical path activities can affect the critical path process.
The above steps provide a practical way of implementing the CPM in project scheduling. However, while following these steps, remember to avoid common pitfalls such as underestimating task durations and failing to account for all dependencies. These could potentially lead to project delays and cost overruns.
Critical Path Method Example
To help you better understand how critical path helps to manage projects, here is an example of how CPM can be used to schedule a project:
A team is tasked with developing a new software product. They break down the project into the following tasks:
Requirements gathering
System design
Implementation
Testing
Deployment
Then, they estimate the duration of each task and identify the dependencies between tasks. For example, task 3 (implementation) cannot start until task 2 (system design) is finished.
The team uses CPM to identify the critical paths in the project. The critical path diagram in this project looks as follows:
requirements gathering --> system design --> implementation --> testing --> deployment
This means that if any of these tasks are delayed, the entire project will be delayed.
The project manager can then use this information to develop contingency plans in case of delays. For example, if there's concern about the risk of delays in the implementation task, they may allocate additional resources to this task or develop a backup plan.
The project manager can also use CPM to monitor and track the actual progress of the project. By comparing the exact start and finish dates of tasks to the planned start and finish dates, it's possible to identify any potential delays.
Finally, the manager can use CPM to communicate the project schedule to other team members involved and stakeholders. By sharing the critical path schedule with the team, the overseer of the critical path can help everyone understand the importance of completing critical tasks on time.
CPM is a powerful tool that can help the project management team to schedule and manage complex projects.
Real-life Applications and Case Studies of the Critical Path Method
The application of the critical path method extends beyond theory and has proven instrumental in various industries. From construction and manufacturing to software development and event planning, CPM's principles have been used to drive project success.
In the world of construction, for example, CPM has been pivotal in managing complex projects. One notable instance is the construction of the Hoover Dam, where the application of CPM principles helped to coordinate a myriad of tasks, ensuring the project was completed ahead of schedule.
In the software industry, tech giants like Microsoft and Google employ CPM in their project management to ensure the timely delivery of updates and new products. By identifying critical tasks and their dependencies, these companies can streamline their workflow and maximize efficiency.
These case studies underscore the versatility and effectiveness of the CPM in managing difficult projects across diverse industries.
The Role of Software Tools in Applying CPM
In the digital age, various software tools have been developed to simplify the application of the critical path method in project scheduling. Tools such as Microsoft Project, Primavera, and Monday.com offer powerful features to automate and streamline the process of CPM implementation.
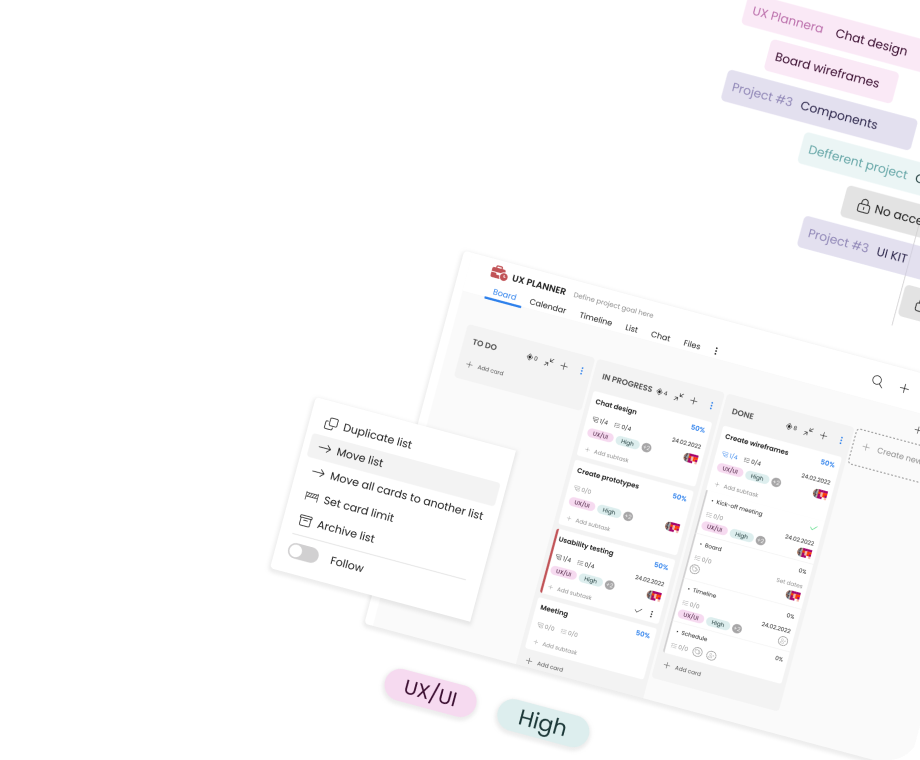
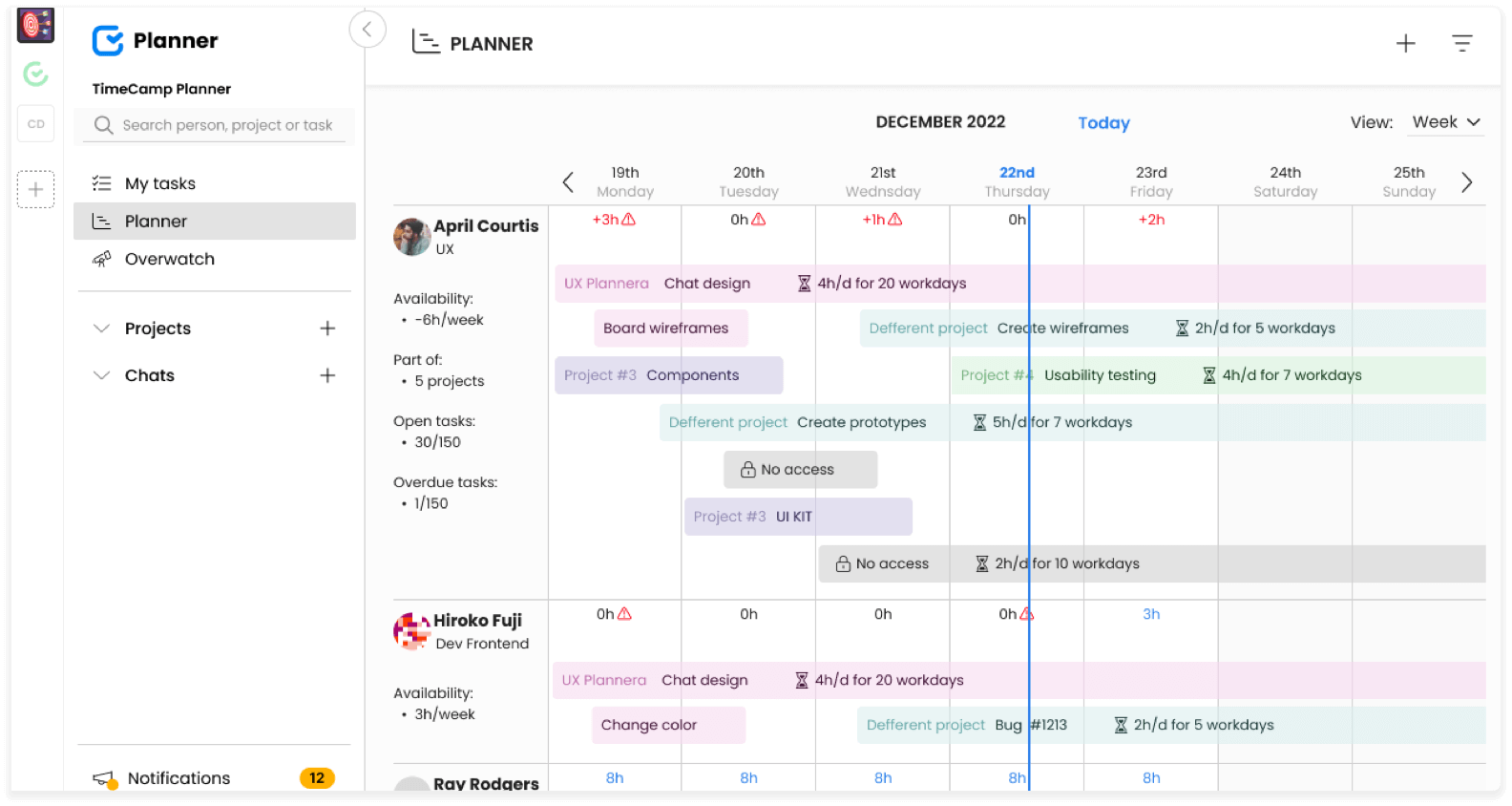
The most common for critical path analysis is project management software, such as Planner by TimeCamp. It can help you in better project management. Here's how you can use it for the Critical Path Method:
-
Define the project scope, compile data from existing projects, and list project activities. Planner allows project managers to define tasks and assign resources.
-
Break down your project into tasks—project managers can use the Kanban boards for the work breakdown structure method to list all the critical path tasks for the whole project.
-
Estimate the Timeline and calculate the length of your project—you can set due dates for all dependent tasks, prioritize tasks, and set planned project completion dates and final project deadlines.
-
Identify task dependencies with the task list for each team member and all project managers.
-
Define different project paths with the Gantt chart and adjust it based on collected data. You can easily alter the entire sequence at every stage when the project progresses without risk for critical tasks and other tasks.
-
Follow recent updates and developments in your critical path method with notifications and real time alerts.
Planner provides an intuitive interface to plan, track, and manage projects efficiently, making the implementation of project's critical path a breeze. It also helps to visualize the critical path method for easier project planning. It's also a good tool to improve team communication and collaboration.
Tips for Project's Critical Path Method
Here are a few practical tips that will help you achieve better results with the critical path method:
-
Use the right project management technique that corresponds with the requirements of the entire project.
-
Implement project management software to keep all the tasks organized in one place and easily monitor progress
-
Have a critical path algorithm for complex, repetitive projects. It'll also help calculate the critical path for future projects.
-
Try time tracking to follow project progress and stick to the deadlines. It's also a great way to track expenses, stay on budget, and keep your project profitable. It's also a good time management technique that can help you better manage your workload.
-
Learn to prioritize tasks so you can better determine task dependencies for your critical path analysis.
-
Work on project management skills to effectively manage your team. Project managers can achieve a lot when they are attentive to the intricacies of the project management world.
Although the critical path method is a standardized approach to managing projects, you can experiment with it and use your favorite tips, tools, and methodologies to optimize work. With your tailored approach, you can achieve more than when sticking to a one, fixed solution.
Use Critical Path for Better Project Management
In conclusion, the critical path method (CPM) is an indispensable tool for effective project scheduling. By shedding light on the critical activities that have a direct impact on the project timeline, it allows for better resource allocation, enhanced productivity, and ultimately, successful project delivery.
While the implementation of CPM requires meticulous planning and precise execution, the benefits it provides make it worth the effort. With the added support of software tools, you can make the CPM in project scheduling even more efficient.
Now that you've gained a comprehensive understanding of the critical path method and its application in project scheduling, it's time to put this knowledge to use. Start applying these principles in your next project, and you're likely to see an improvement in project timelines and resource utilization. Remember, effective project management is an art, and tools like CPM are the brushes that allow you to paint the picture of success.
Feel free to share your experiences of applying CPM in project scheduling, or if you have any questions or need further clarification, don't hesitate to reach out.
Happy project managing, and here's to achieving project success with CPM!